I-Team In-Depth
The Unknown Puts Offspring At Risk Of Sickle Cell Disease
|
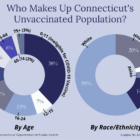
Most Connecticut residents who carry a trait for sickle cell disease don’t know it, resulting in thousands of people unwittingly risking having a child born with the debilitating illness, according to sickle cell disease specialists. The reasons for this vary: there’s a lack of knowledge about results of newborn testing for the trait, parents don’t always convey test results to their children, gaps in state record keeping, and state records that identify people with the disease or trait only go back to 2012. Also, doctors typically only test for the trait when a patient requests it. And people often don’t know they can have the trait even when sickle cell disease isn’t in their family. Dr. Biree Andemariam, director of the New England Sickle Cell Institute at UConn Health, said physicians should include trait testing in routine exams. “It should be standard care,” she said.