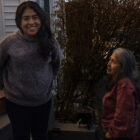Disparities
The Pandemic Changed Their Lives – And Brought Them Closer Together
|
A patch of dirt in the northwest corner of their back yard, bounded by a chain link fence, a stone wall and a garage that houses feral cats, has become a happy place for Gladis Castro, 57, and her daughter Carla, 27. The Danbury mother and daughter have found purpose and meaning, and built a strong relationship, in a simple garden that has connected them with nature, given them food and provided a diversion from the COVID-19 pandemic. Just being outdoors has become increasingly important to them in caring for their long-term respiratory effects from the virus. Inhaling the early-morning air while working in her garden often reminds Gladis Castro of Santa Isabel, her village in the Andes mountains of Ecuador. After a morning summer walk the two made smoothies with freshly picked red raspberries from their garden.