Medical Practices Become Another Pandemic Casualty
|
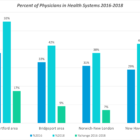
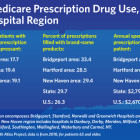
After 35 years as an oral surgeon, Dr. Arthur Wilk closed his practice in Clinton following “daunting challenges” caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. In Darien, Dr. Cecile Windels sold her pediatric practice to a hospital health system after enduring significant income losses. They are among thousands of physicians and other health care professionals across the country who have made coronavirus-prompted career changes such as closing practices, joining larger health systems and retiring early. The reasons for the moves vary from declines in income due to fewer inpatient visits to increased operational costs for personal protective equipment (PPE) and fears of contracting the coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2. Health care advocates say the changes will exacerbate physician shortages, further erode the existence of private practices, decrease patient choice of doctors and obstruct continuity of patient care. A January report in Health Affairs, a peer-reviewed journal of health policy research, said: “Consolidation tends to lead to higher prices without strong evidence of quality improvements.”
“The national trends are definitely happening in Connecticut,” said Dr. Gregory Shangold, president of the Connecticut State Medical Society.