I-Team In-Depth
Binge, Heavy Drinking Rates Rise In State, Especially For Women
|
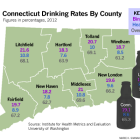
Rates of heavy drinking in Connecticut spiked 21.3 percent between 2005 and 2012, while binge-drinking rates rose nearly 14 percent, with the largest increases among women drinkers, a new report shows. The increases put Connecticut’s drinking rates above the national average, with survey data from some counties showing that more than one in five adults are binge drinkers — defined as consuming more than four drinks a day for women and five for men on at least one occasion in the past 30 days. Heavy drinking and binge drinking rates were highest in Litchfield and Middlesex counties and lowest in New Haven and Hartford counties. All of the state’s counties exceeded the national rate for any alcohol consumption – 65.3 percent of adults statewide, compared to the national rate of 56 percent. While Connecticut had higher-than-average rates in 2012, so did a number of other states in the Northwest, Midwest, and New England.