I-Team In-Depth
Can Independent Primary Care Doctors Survive Dominance of Hospital Health Systems?
|
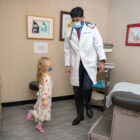
Every day, Dr. Leslie Miller of Fairfield thinks about selling her practice to a hospital health system. “Everybody who is in this environment thinks every day of throwing in the towel and joining a hospital,” said Miller, a sole practitioner in primary care for 20 years. “The business side is the problem,” she said, referring to expensive and time-consuming requirements of medical insurance and government regulations. Dr. Khuram Ghumman took the unusual route of working in a hospital system first, then going into private primary care practice because he objects to the “corporatization” of health care. He said conflicts of interest can arise if an owner and its employed physicians have different objectives.